SMARTCHEM FROM ROW2 TECHNOLOGIES
Are you aware of any Chemical Database which offers one stop solution to the Sourcing, R&D and Business Development department? Explore Smartchem to Quickly find Suppliers (Procurement), Customers (BD) & Synthetic pathways (R&D)
Is this the information you looking for? Evaluate SmartChem, lets schedule a demo. Try us once. You will use us for life.
Anand Ramakrishnan |Vice President – Sales & Operations | +91 9821384045 | +1 973-795-1141 | ranand@row2technologies.com | http://www.row2technologies.com | WhatsApp: +91 9821384045
Anthony Crasto | Advisor | +91 9321316780 | c_acrasto@row2technologies.com | amcrasto@gmail.com | www.row2technologies.com | WhatsApp: +91 9321316780 |
‘Top 10 Prominent & Great Personalities of the year 2022’ campaign by Fame Finders. ANTHONY CRASTO

‘Top 10 Prominent & Great Personalities of the year 2022’ campaign by Fame Finders.
Feeling great to be selected in the ‘Top 10 Prominent & Great Personalities of the year 2022’ campaign by Fame Finders. It is an online campaign to honour inspiring personalities and feature them in the upcoming edition of the top news sites, including – Deccan Chronicle/Asian Age/Deccan Herald, ANI, Zee5, Latestly, Lokmat Times, DailyHunt, Google News, JioNews, MSN and 70+ sites.Jan 16 2023

ARIMOCLOMOL

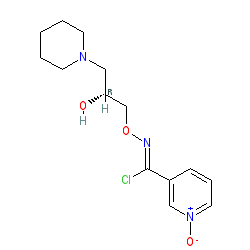
ARIMOCLOMOL
アリモクロモル;
| Formula | C14H20ClN3O3 |
|---|---|
| Exact mass | 313.1193 |
| Mol weight | 313.7799 |
CAS289893-25-0
289893-26-1 (Arimoclomol maleate);
INN 8300
N-[(2R)-2-hydroxy-3-piperidin-1-ylpropoxy]-1-oxidopyridin-1-ium-3-carboximidoyl chloride
BRX 220
Arimoclomol maleate is in a phase III clinical trials by Orphazyme for the treatment of Niemann-Pick disease type C (NP-C). It is also in phase II clinical studies for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Arimoclomol(INN; originally codenamedBRX-345, which is a citrate salt formulation ofBRX-220) is an experimental drug developed byCytRx Corporation, a biopharmaceutical company based inLos Angeles, California. In 2011 the worldwide rights to arimoclomol were bought by Danish biotech company Orphazyme ApS.[1]TheEuropean Medicines Agency(EMA) andU.S. Food & Drug Administration(FDA) granted orphan drug designation to arimoclomol as a potential treatment forNiemann-Picktype C in 2014 and 2015 respectively.[2][3]
| Fig. 1Structures of (±)-bimoclomol (1) and (R)-(+)-arimoclomol… |
View original post 2,390 more words
LANSOPRAZOLE


Lansoprazole
- Molecular FormulaC16H14F3N3O2S
- Average mass369.362 Da
Lansoprazole, AG-1749, ABT-006, CG-4801, A-65006, Ogast, Lanzor, Lanzo, Agopton, Opiren, Bamalite, Takepron, Lansox, Lansox, Ogastro, Monolitum, Prevacid, Zoton103577-45-3[RN]
1H-Benzimidazole, 2-[[[3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-2-pyridinyl]methyl]sulfinyl]-
лансопразол[Russian][INN],لانسوبرازول[Arabic][INN],兰索拉唑[Chinese][INN]
CAS Registry Number:103577-45-3
CAS Name:2-[[[3-Methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoro-ethoxy)-2-pyridinyl]methyl]sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole
Additional Names:2-(2-benzimidazolylsulfinylmethyl)-3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)pyridine
Manufacturers’ Codes:A-65006; AG-1749
Trademarks:Agopton (Takeda); Lansox (Takeda); Lanzor (Aventis); Limpidex (Sigma-Tau); Ogast (Takeda); Prevacid (TAP); Takepron (Takeda); Zoton (Wyeth)
Molecular Formula:C16H14F3N3O2S,Molecular Weight:369.36
Percent Composition:C 52.03%, H 3.82%, F 15.43%, N 11.38%, O 8.66%, S 8.68%
Literature References:Gastric proton-pump inhibitor. Prepn: A. Nohara, Y. Maki,EP174726;eidem,US4628098(both 1986 to Takeda).HPLC determn in plasma: T. Unoet al.,J. Chromatogr. B816, 309 (2005). Pharmacology: H. Satohet al.,J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.248,806 (1989). Mechanism…
View original post 3,935 more words
MAX 40279
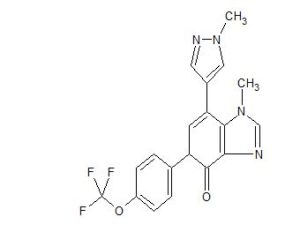
MAX 40279,EX-A4057
Max 4; MAX-40279; MAX-40279-001; MAX-40279-01
UNII-DL772G3NN7
2070931-57-4
C22H23FN6OS,438.5
7-(4-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-6-methyl-N-(1-piperidin-4-ylpyrazol-4-yl)thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-amine
Thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-amine, 7-(4-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-6-methyl-N-[1-(4-piperidinyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]-

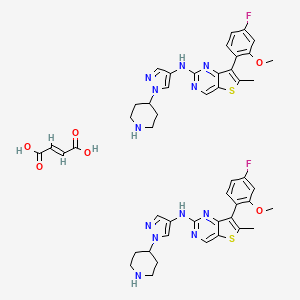
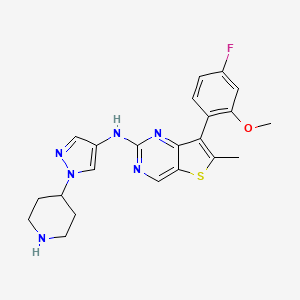
7-(4-FLUORO-2-METHOXYPHENYL)-6-METHYL-N-(1-(PIPERIDIN-4-YL)-1H-PYRAZOL-4-YL) THIENO (3,2-D)PYRIMIDIN-2-AMINE SEMI-FUMARATE CAS2388506-43-0
- 7-(4-Fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)-6-methyl-N-[1-(4-piperidinyl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-2-amine
- OriginatorMaxinovel Pharmaceuticals
- ClassAntineoplastics
- Mechanism of ActionFibroblast growth factor receptor antagonists; Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 inhibitors
- Orphan Drug StatusYes – Acute myeloid leukaemia
- Phase IAcute myeloid leukaemia; Solid tumours
Most Recent Events
- 28 Nov 2019Phase-I clinical trials in Solid tumours (Late-stage disease, Metastatic disease) in China (PO) (NCT04183764)
- 16 Apr 2019Phase-I clinical trials in Acute myeloid leukaemia (Second-line therapy or greater) in China (PO) (NCT04187495)
- 23 Jan 2019Guangzhou Maxinovel Pharmaceuticals plans a phase I trial in China (ChiCTR1900020971)
- MaxiNovel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Announces FDA Orphan Drug Designation for MAX-40279 for the Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
March 29, 2018 11:24 AM Eastern Daylight Timehttps://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20180329005826/en/MaxiNovel-Pharmaceuticals-Inc.-Announces-FDA-Orphan-Drug-Designation-for-MAX-40279-for-the-Treatment-of-Acute-Myeloid-Leukemia-AML
GUANGZHOU, China–(BUSINESS…
View original post 4,078 more words
Lurbinectedin

Lurbinectedin
(1’R,6R,6aR,7R,13S,14S,16R)-5-(Acetyloxy)-2′,3′,4′,6,6a,7,9′-decahydro-8,14-dihydroxy-6′,9-dimethoxy-4,10,23-trimethyl-spiro(6,16-(epithiopropaneoxymethano)-7.13-imino-12H-1,3-dioxolo[7,8]soquino[3,2-b][3]benzazocine-20,1′-[1H]pyrido[3,4-b]indol]-19-one
| Molecular Weight | 784.87 |
| Formula | C41H44N4O10S |
| CAS No. | 497871-47-3 (Lurbinectedin); |
| Chemical Name | Spiro[6,16-(epithiopropanoxymethano)-7,13-imino-12H-1,3-dioxolo[7,8]isoquino[3,2-b][3]benzazocine-20,1′-[1H]pyrido[3,4-b]indol]-19-one, 5-(acetyloxy)-2′,3′,4′,6,6a,7,9′,13,14,16-decahydro-8,14-dihydroxy-6′,9-dimethoxy-4,10,23-trimethyl-, (1’R,6R,6aR,7R,13S,14S,16R)- (9CI) |
fda approved , 6/15/2020,ZEPZELCA, Pharma Mar S.A.
To treat metastatic small cell lung cancer
Drug Trials Snapshot
Research Code:PM-01183;PM-1183
MOA:RNA polymerase inhibitor
Indication:Ovarian cancer;Breast cancer;Non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)лурбинектединلوربينيكتيدين芦比替定(1R,1’R,2’R,3’R,11’S,12’S,14’R)-5′,12′-Dihydroxy-6,6′-dimethoxy-7′,21′,30′-trimethyl-27′-oxo-2,3,4,9-tetrahydrospiro[β-carboline-1,26′-[17,19,28]trioxa[24]thia[13,30]diazaheptacyclo[12.9.6.13,11…2,13.04,9.015,23.016,20]triaconta[4,6,8,15,20,22]hexaen]-22′-yl acetate[ACD/IUPAC Name]2CN60TN6ZS497871-47-3[RN]9397
Lurbinectedin is in phase III clinical development for the treatment of platinum refractory/resistant ovarian cancer.
Phase II clinical trials are also ongoing for several oncology indications: non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, small cell lung cancer, head and neck carcinoma, neuroendocrine tumors, biliary tract carcinoma, endometrial carcinoma, germ cell tumors and Ewing’s family of tumors.
Lurbinectedin, sold under the brand nameZepzelca, is a medication for the treatment of adults with metastatic small cell lung cancer (SCLC) with disease progression on or after…
View original post 4,925 more words
AK 3280
AK-3280
AK 3280; GDC3280; RG 6069
C19 H15 F3 N4 O2, 388.34
CAS 1799412-33-1
4H-Benzimidazol-4-one, 1,5-dihydro-1-methyl-7-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-5-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]-
Ci8Hi4N502F3, mass 389.3 g/mol),
ROCHE,
Ark Biosciences , under license from Roche , is developing AK-3280, an antifibrotic agent, for the potential oral treatment of IPF. In July 2018, Ark intended to further clinical development of the drug, for IPF. In June 2019, a phase I trial was planned in Sweden.
- Originator Genentech
- Mechanism of Action Undefined mechanism
- Phase I Interstitial lung diseases
- 19 Jun 2019Ark Biosciences plans a phase I trial for Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (In volunteers) in Sweden (PO, Tablet), in August 2019 , (NCT03990688)
- 28 Sep 2018GDC 3280 is still in phase I trials for Interstitial lung diseases (Genentech pipeline, September 2018)
- 28 Jun 2018No recent reports of development identified for phase-I development in Fibrosis(In…
View original post 3,170 more words
SRT 1720

SRT-1720 diHCl
CAY10559
CAS: 1001645-58-4 (di HCl) , 925434-55-5 (free base) 1001645-58-4 (HCl)
Chemical Formula: C25H25Cl2N7OS
Molecular Weight: 542.483
Elemental Analysis: C, 55.35; H, 4.65; Cl, 13.07; N, 18.07; O, 2.95; S, 5.91
SRT-1720 HCl, SRT-1720 hudrochloride; SRT1720; SRT-1720; SRT 1720; CAY10559; CAY-10559; CAY 10559; SIRT-1933; SIRT 1933; SIRT1933.
N-(2-(3-(piperazin-1-ylmethyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazol-6-yl)phenyl)quinoxaline-2-carboxamide dihydrochloride

- Molecular FormulaC25H23N7OS
- Average mass469.561 Da
SRT-1720, also known as CAY10559 and is a drug developed by Sirtris Pharmaceuticals intended as a small-molecule activator of the sirtuin subtype SIRT1. It has similar activity in the body to the known SIRT1 activator resveratrol, but is 1000x more potent. In animal studies it was found to improve insulin sensitivity and lower plasma glucose levels in fat, muscle and liver tissue, and increased mitochondrial and metabolic function. A study of SRT1720 conducted by the National Institute on Aging found that the drug may extend the lifespan…
View original post 1,417 more words
Thiotepa, チオテパ ,тиотепа , ثيوتيبا , 塞替派 ,
Thiotepa, チオテパ
- Use:antineoplastic, alkylating agent
- Chemical name:1,1′,1”-phosphinothioylidynetrisaziridine
- Formula:C6H12N3PS
- MW:189.22 g/mol
- CAS:52-24-4
- EINECS:200-135-7
- LD50:14500 μg/kg (M, i.v.); 38 mg/kg (M, p.o.);
9400 μg/kg (R, i.v.) - Aziridine, 1,1′,1”-phosphinothioylidynetris-Aziridine, 1-[bis(1-aziridinyl)phosphinothioyl]-N,N’,N”-TriethylenethiophosphoramidePhosphorothioic tri(ethyleneamide)SZ2975000T3NTJ APS&- AT3NTJ&- AT3NTJ [WLN]ThiofozilThiotef1,1′,1”-Phosphorothioyltriaziridine
JAPAN APPROVED, Rethio, PMDA, 2019/3/26
тиотепа [Russian] [INN]
ثيوتيبا [Arabic] [INN]
塞替派 [Chinese] [INN]
Thiotepa (INN,[1] chemical name: N,N′,N′′-triethylenethiophosphoramide) is an alkylating agent used to treat cancer.
Thiotepa is an organophosphorus compound with the formula SP(NC2H4)3.[2] It is an analog of N,N′,N′′-triethylenephosphoramide (TEPA), which contains tetrahedral phosphorus and is structurally akin to phosphate. It is manufactured by heating aziridine with thiophosphoryl chloride.
History
Thiotepa was developed…
View original post 800 more words